Which Inverter is Better? A Comprehensive Comparison between Hybrid Inverters and Ordinary Inverters
In the selection of energy equipment, the type of inverter directly affects the stability and efficiency of power supply. Understanding the differences between different types of inverters is crucial for choosing a suitable product. This article will deeply explore the classification of inverters, focus on comparing the characteristics of hybrid inverters and ordinary inverters, and extend the analysis of relevant types of solar inverters to help you make a better decision. Meanwhile, through practical application cases, you can have a more intuitive understanding of the value of inverters in different scenarios.
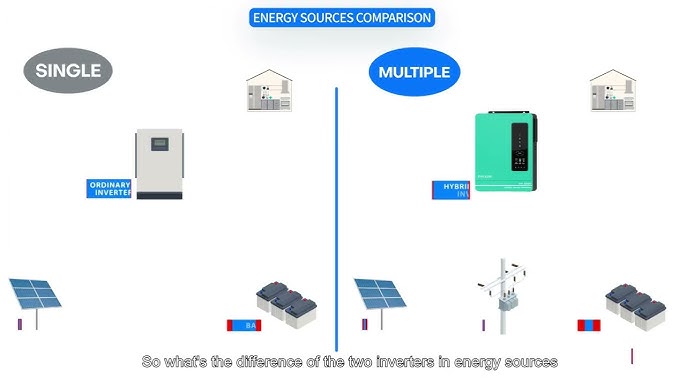
The core function of an inverter is to convert direct current (DC) output from power sources such as batteries and solar panels into alternating current (AC) to meet the power consumption needs of household and commercial appliances. Based on different application scenarios, inverters are mainly divided into solar inverters and ordinary inverters.
Solar inverters are specifically designed for solar systems and usually have built-in components such as a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) controller. The MPPT controller can track the maximum power output point of the solar panel in real-time. By dynamically adjusting the voltage and current, it ensures that the solar panel operates at high efficiency. Ordinary inverters are independent devices, lack a built-in controller, and have no hybrid grid connection function. They are mostly applied to power supply systems that do not involve solar panels. In addition, solar inverters are also known as off-grid inverters or hybrid inverters. With functions such as battery charging and grid connection, they can be flexibly applied in residential and commercial scenarios.
Efficiency is an important indicator distinguishing the two types of inverters. Solar inverters can fully tap the power generation potential of solar panels with the help of the MPPT algorithm, ensuring their continuous and efficient operation and increasing the overall power generation. In contrast, ordinary inverters are prone to energy loss during the conversion from DC to AC due to the lack of such optimization technology, reducing the power utilization rate.
In terms of price, solar inverters are usually more expensive than ordinary inverters, but the environmental value and long-term economic benefits they bring cannot be ignored. Using solar inverters can significantly reduce carbon emissions, which is in line with the concept of green development. Over time, the electricity costs saved can gradually offset the higher upfront equipment investment. From a long-term perspective, it is a choice that combines environmental protection and economic efficiency.
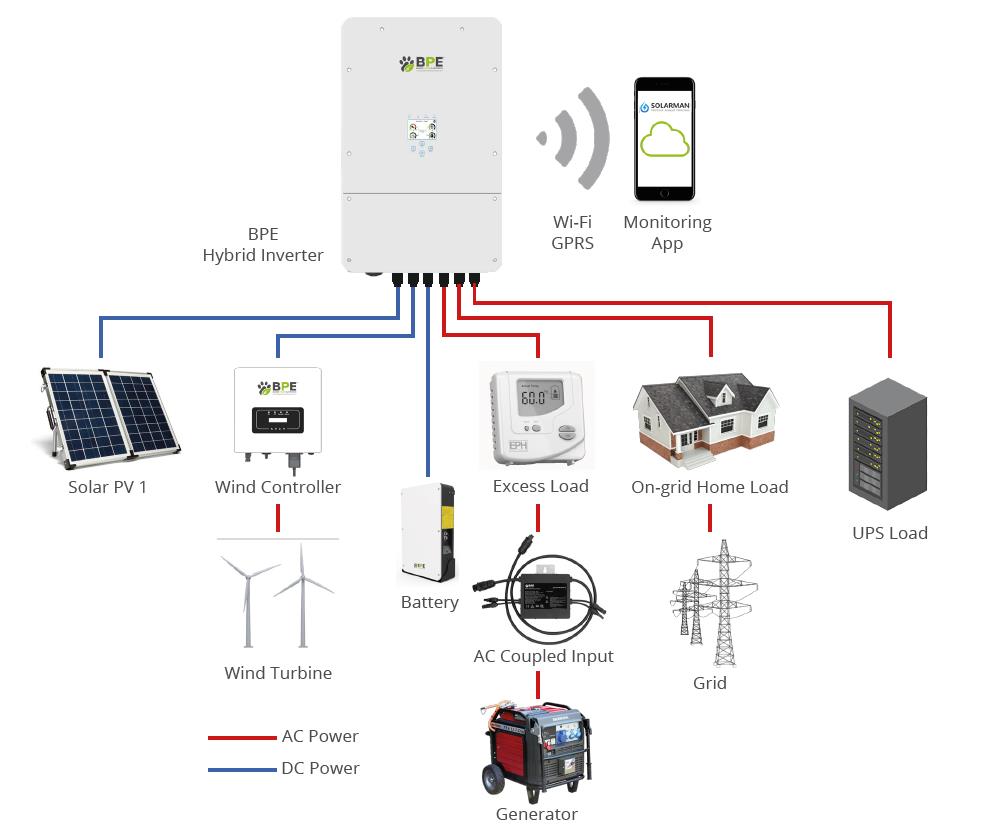
After clarifying the differences between solar inverters and ordinary inverters, a further comparison between hybrid inverters and ordinary inverters can more clearly show their advantages and disadvantages in practical applications.
The greatest advantage of hybrid inverters lies in the diversity of energy utilization. They can integrate multiple energy sources such as solar energy, batteries, utility power, and generators. With a built-in MPPT controller, they can intelligently optimize the energy configuration, effectively reducing the dependence on the traditional power grid. In terms of efficiency, hybrid inverters can usually reach 90% - 98%, while the efficiency of ordinary inverters is mostly in the range of 80% - 90%. The high efficiency of hybrid inverters is obvious.
Battery energy storage is another major difference between the two. Hybrid inverters are equipped with a multi-functional battery energy storage system, which can store surplus electricity from solar power generation and grid power for use at night or during power outages. Moreover, hybrid inverters integrated with an MPPT controller support different operating modes with or without a battery, providing users with flexible battery configuration solutions and helping to control costs. Ordinary inverters not only require an additional battery energy storage system but also have shortcomings in battery charging efficiency.
Modern hybrid inverters generally have a remote monitoring function, allowing users to grasp the energy production and usage in real-time through mobile phones or other terminals. This function is convenient for timely discovery of system problems and optimization of energy efficiency. In contrast, ordinary inverters usually do not have a remote monitoring capability and are somewhat insufficient in intelligent management.
Solar inverters include types such as off-grid inverters, hybrid inverters, and grid-connected inverters, each suitable for different application scenarios.


Through a comprehensive comparison of different types of inverters and practical case analysis, it can be found that hybrid inverters show stronger applicability in most scenarios with their advantages such as energy flexibility, efficient energy storage, and intelligent monitoring; ordinary inverters are suitable for scenarios with relatively simple functional requirements. When making an actual selection, users should comprehensively evaluate and choose the most suitable inverter product according to their own power consumption needs, usage scenarios, and budget.
Address : Room 305, Tower B, Yinuo Business Center, intersection of West Second Ring Road and Hehuan Road, Bijiashan Street, Shushan District, Hefei city, Anhui Province
Please read on, stay posted, subscribe, and we welcome you to tell us what you think.
Links: Inverter Cables
Cowellxm
Copyright 2026 @ Anhui Solarasia Energy Technology Co.,Ltd .All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Blog | XML | Privacy Policy
 Network Supported
Network Supported